 TOC |
GI
TOC |
GI

Hepatitis Serology
Markers
Five forms of viral hepatitis
| Hepatitis |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
| Virus |
HAV |
HBV |
HCV |
HDV |
HEV |
| Family |
Picornavirus |
Hepadnavirus |
Flavivirus |
Satellite |
Calicivirus |
| Genome |
ssRNA |
dsDNA |
ssRNA |
ssRNA |
ssRNA |
| Spread |
Fecal-oral |
parenteral, sexual,perinatal |
parenteral, ?sexual |
parenteral, ?sexual |
Fecal-oral |
| Antigens |
HAV-Ag |
HbsAg,HBcAg,HBeAg |
HCV-Ag |
HDV-Ag |
HEV-Ag |
| Antibodies |
Anti_HAV |
Anti-HBs,Anti-HBc,Anti-HBe |
Anti-HCV |
Anti-HDV |
Anti-HEV |
| Virus markers |
HAV RNA |
HBV DNA, DNA polymerase |
HCV RNa |
HDV RNa |
viruslike partiacles |
Semin.Liver Ds. 11:74,1991, Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc
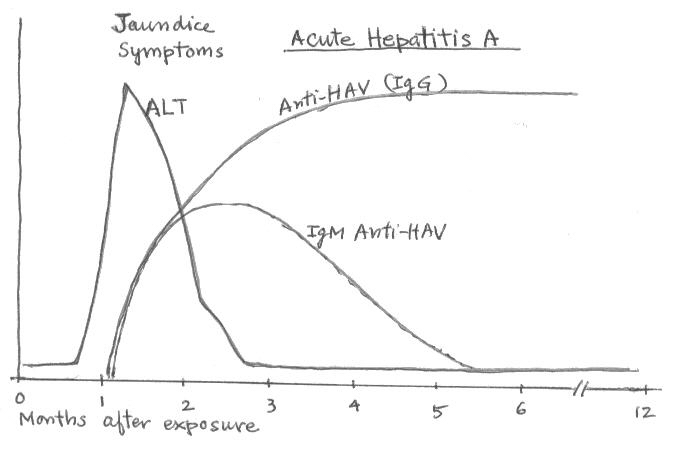
Hepatitis A Serology
-
anti-HAV (antibody to hepatitis A
virus)
it detects total antibody of both IgG and IgM sublasses of HAV. Its
presence indicates either acute or resolved infection.
-
IgM anti-HAV (IgM antibody subclass of anti-HAV,
hepatitis A virus)
it indicates a recent infection with HAV (< 6months). It is used
to diagnose acute hepatitis A
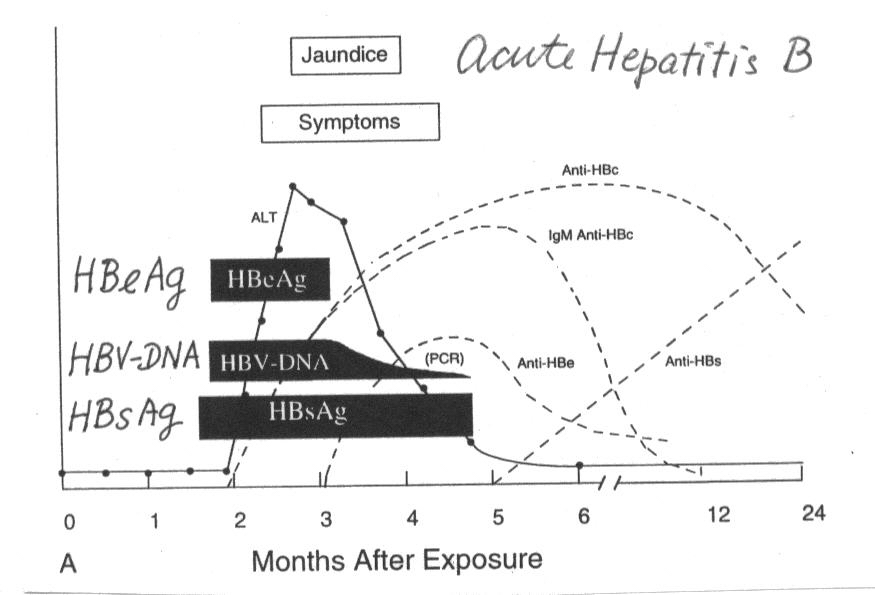
Hepatitis B Serology
-
HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen)
it indicates either acute or chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
-
anti-HBs (HBsAb = antibody to hepatitis B surface
antigen)
it is a marker of hepatitis B immunitiy.
-
anti-HBc (HBcAb = antibody to hepatitis B core
antigen)
it is a nonspecific marker of acute, chronic, or resolved HBV infection.
It is not a marker of faccine-induced immunity.
-
IgM anti-HBc (IgM antibody sublass of
anti-HBc)
it indicates recent infection with HBV (<6 months). Its presence
indicates acute infection.
-
HBeAg (Hepatitis B "e" antigen)
it is a marker of a high degree of HBV infectivity, & acorrelates with
a high level of HBV replicaiton. It is primarily used to help determine
the clinical management of patients with chronic HBV infection.
-
anti-HBe (antibody to hepatitis B "e"
antigen)
it may be presnet in an infected or immune person. In persons with
chronic HBV infection, its presence suggests a low viral titer and a low
degree of infectivity.
-
HBV-DNA (HBV deoxyribonucleic acid)
it is a marker of viral replication. It correlates well with infectivity.
It is used to assess and monitor the treatment of patients with chronic
HBV infection.
Hepatitis C Serology
-
anti-HCV (antibodies to HCV - hepatitis C Virus)
by ELISA or RIBA-2 assay
to detect acute & chronic hepatitis C infection
-
Serum HCV RNA qualitative & quantitative assay
by PCR method
to establish viremia & is employed in the management of chronic HCV infection
-
Genotyping of HCV RNA (genotype 1-less
Rx responsiveness, or genotype 2 or 3 with better Rx responsivenss)
The 1998 studies of interferon and ribavirin combination therapy
showed important differences in the outcome based on genotype; that
is, approximately 30% of patients with genotype 1 and approximately
65% with genotype 2 or 3 had sustained virologic responses. In addition,
patients with genotype 1 had higher rates of sustained virologic response
with 48 weeks of combination therapy than with 24 weeks of therapy, whereas
patients with other genotypes achieved no additional benefit beyond 24 weeks
of therapy. These studies have led to the practice of administering
therapy for 12 months to patients with genotype 1 but for only 6 months to
those with genotype 2 or 3. Factors in addition to genotype are known to
predict the likelihood of successful therapy with ribavirin and interferon.

Back-to-top |
Home Page
10262004


